Rainwater itself is one of the purest forms of water nature provides. However, whether it is safe to drink depends on several factors.
In its journey from sky to ground, rainwater can pick up contaminants such as dust, smoke, and pollutants from the air, as well as bacteria, parasites, and chemicals from surfaces it lands on, like rooftops and roads.
With climate change affecting water availability in many regions, rainwater harvesting presents an opportunity to reduce reliance on municipal water supplies and promote self-sufficiency.
The Rise of Rainwater Harvesting
Households in Auckland typically spend more than $1000 each year on water services, raising questions about the efficiency of using drinking-quality water for non-potable uses like flushing toilets or watering gardens. Moreover, industrial facilities often require significant amounts of water, particularly those with large non-absorbent areas.
Homeowners and industrialists are increasingly aware of the impact of their water consumption on the planet, and they are seeking sustainable alternatives to traditional water sources.
Collecting rainwater offers a promising solution, providing a renewable resource that can be utilized for various purposes, including drinking. In places like Australia and the U.S., water scarcity has spurred the development of technologies for maximizing stormwater (also called rainwater) reuse.

This practice involves capturing rainwater that falls on rooftops, directing it into storage systems, and treating it for safe usage. This process is known as rooftop rainwater harvesting.
The United Nations Agenda 2030 reports that more than 2 billion people reside in regions facing severe water stress. In this context, rooftop rainwater harvesting plays a crucial role in decreasing reliance on traditional water sources and aiding in the conservation of groundwater and surface water resources.
Benefits of Drinking Rainwater
Drinking rainwater, when properly harvested and treated, comes with several notable advantages. Firstly, rainwater is naturally pure, as it originates from the sky and is free from the contaminants often found in ground or surface water. This purity makes it an attractive option for those concerned about the quality of their tap water.
Additionally, rainwater typically has low mineral content, which can be beneficial for individuals looking to reduce their intake of certain minerals, such as sodium or fluoride. This can be particularly relevant for people with specific dietary needs or health concerns.
From an environmental perspective, utilizing rainwater for drinking purposes reduces the strain on local water resources.
Furthermore, by adopting rainwater harvesting practices, households can contribute to water conservation efforts and minimize their ecological footprint.
Risks and Concerns
One of the primary concerns with rainwater is contamination from air pollutants, which can be present in the atmosphere and mix with raindrops as they fall. This is especially true in urban areas with high levels of industrial activity.
Bird droppings and other organic debris on rooftops can introduce harmful bacteria and pathogens into collected rainwater.
Microbial growth within storage systems can further compromise the water’s safety if not properly managed.
It’s crucial to recognize these risks and take appropriate measures to address them, ensuring that rainwater remains a safe and viable option for drinking.
Ensuring the Safety
But, is rainwater safe to drink from the sky? Definitely a NO!
To make rainwater safe for consumption, several steps must be taken. Proper storage and filtration systems are vital components of any rainwater harvesting setup.
Collectors should be designed to prevent debris from entering storage tanks, and first-flush diverters can help redirect the initial runoff, which may contain contaminants, away from the collection system.

Filtration is another critical aspect, as it can remove impurities and pathogens from the water.
Ultraviolet (UV) sterilization or boiling rainwater is recommended to eliminate harmful microorganisms, providing peace of mind for those using rainwater for drinking.
Rainwater Harvesting and Treatment Guide
Implementing best practices for harvesting, storing, and treating rainwater is essential for maintaining its quality and safety.
– Start by selecting a suitable collection surface, such as a clean rooftop, free from harmful materials like lead or asbestos.
– Regular maintenance of the collection system, including cleaning gutters and storage tanks, is necessary to prevent contamination.
– Proper filtration and treatment processes, such as UV sterilization or boiling, should be employed to ensure the water’s safety.
– Monitoring the quality of the collected rainwater through periodic testing is also advisable.
Monitoring allows homeowners to detect any changes in the water’s composition and adjust their treatment methods accordingly.
Global Case Studies
1. India: Reviving Ancient Practices
In the arid regions of Rajasthan, India, the age-old practice of rainwater harvesting has been brought back to life. The city of Jaipur stands as a testament to this, where traditional water structures have been rejuvenated to tackle the issue of water scarcity.
2. South Africa: Turning Crisis into Opportunity
In 2018, Cape Town faced a severe water crisis. This led to the promotion of rainwater harvesting, with a successful initiative being the implementation of Greywater Recycling Systems. These systems, combined with rainwater harvesting in homes, have significantly reduced the dependence on the municipal water supply.
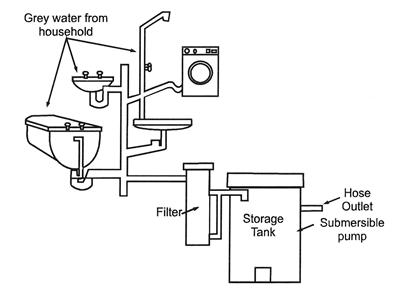
3. Mexico City: Community-led Initiatives
Mexico City has turned to rainwater harvesting to address its water scarcity issues. A notable initiative is the Isla Urbana project, a community-led effort that has been installing rainwater harvesting systems in households across the city.
4. New Zealand: Island-wide Adoption
On Waiheke Island in New Zealand, the majority of properties have rainwater collection systems due to the island’s reliance on tank water. The Waiheke Resources Trust promotes this practice through educational initiatives and provides guidance on the installation and maintenance of these systems.
5. USA: Incentivizing Rainwater Harvesting
The city of Tucson in Arizona, known for its arid climate, has made significant strides in the implementation of rainwater harvesting. The Tucson Rainwater Harvesting Rebates Program offers financial incentives for residents and businesses to install rainwater harvesting systems with a rebate up to $2,000 for residential rainwater-harvesting systems.
Bottomline
In conclusion, rainwater can be a safe and sustainable source of drinking water when collected and treated properly.
The benefits of rainwater harvesting, from its purity and low mineral content to its positive impact on the environment, make it a compelling choice for eco-conscious homeowners, sustainability advocates, and health enthusiasts.
By following recommended guidelines and implementing best practices, individuals can enjoy the advantages of rainwater while minimizing potential risks.
- Saini, R. K., Chowdhury, Y., & Kumar, M. (2016). Roof Top Rain Water Harvesting in Rural Areas: A Case Study of Vidhani Village, Jaipur. IJERTCONV4IS23046, 2278-0181.
- https://roofinsulations.co.za/grey-water-harvesting/?srsltid=AfmBOorPIWTRTPFD–ceh-fOCyKuQs1UzNn1bFVBRFsLKFsZiPLCOCsC
- https://islaurbana.org/en/
- https://www.waternz.org.nz/Article?Action=View&Article_id=845
- https://watershedmg.org/learn/classes/rebate










I saw a lot of website but I think this one has something extra in it in it